Information Security, the new buzzword these days, comprises several sub-departments and functionalities. Generally, the Information Security team is divided into two sub-teams, the Red team and the Blue team. In this article, we will discuss in detail both the Red and Blue team, their functionalities, and what initial knowledge base you need to have to land an entry-level job for either of them.
Red Team:
A Red team consists of individuals who mimic themselves as adversaries and try to bypass all the security controls in place for an organization. Whether it be physical or logical controls, they analyze the environment, generates the attack surfaces unique to a particular organization, and then assess all the security controls that objectively are in place.
Red teamers are highly skilled technical individuals often known as “Ethical Hackers.” As they try to compromise an environment ethically. They often use known vulnerabilities, security misconfigurations, 0-day exploits, and a “hacker” mindset to bypass the existing security controls, whether access controls, authorization control, physical security, etc. They will consider each path that can lead to compromise an organization.
How Red Team works:
A red team works almost the same as a sophisticated adversary will work. They will follow specific steps to carry out a successful attack against a target. Below Red Team, methodology from Fire Eye clearly states these steps:
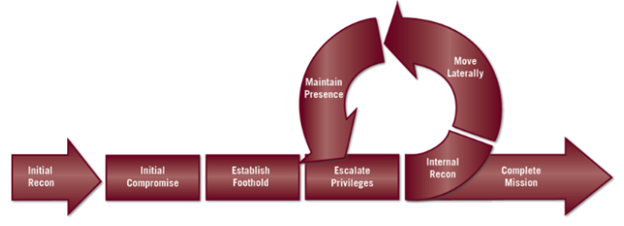
Initial Recon:
This is the most crucial phase for any red team exercise. This will either make it or break it. In this phase, red teamers do both manual and automated reconnaissance against the agreed scope of an enterprise. They will look from the birds-eye view on things that are in range and see how anything can help them get target-related information.
Initial Compromise:
In this phase of the exercise, they will use various automated and manual techniques to gain initial compromise against the target host. Tools may include but are not limited to NMAP, Nessus, OpenVAS, and Shodan, etc. In addition, red teamers will look into the common misconfigurations and CVEs to exploit for gaining initial compromise.
Establish Foothold:
After successfully gaining the initial compromise, red teamers will further establish the foothold with the persistent backdoors. They will make sure their malicious backdoors can efficiently communicate with the C2 servers, and remote commands can be executed through the malicious binaries.
Escalate Privileges:
Once a persistence backdoor has been established, now the next step will be escalating privileges. It is an essential step during the exercise, and our further success depends upon it. During this phase, we will analyze what privileges we hold currently. We will also assess how we can escalate ourselves from a low privileged user to a high privileged user and, in an ideal case, “Domain Admin.” Domain Admins are the highest privileged user in Windows Active Directory Environment, and while in *nix environment, we aim to escalate our privileges to a “Root” user.
Cyclic Process of Internal Recon, Lateral Movement and Maintain Persistence:
We do surveillance of the compromised network, sniff the network traffic and look for sensitive hosts in a cyclic process. We also move laterally into the environment, try to jump on various parts of the network, and gathers as much information as possible. Finally, once we have found anything of our interest, we try to maintain persistent access on that particular host and then escalate our privileges on that host as well.
This is a cyclic process and keeps on going until we are satisfied with the level of access and information we have accessed.
Complete Mission:
It is the final part of our exercise, where we almost conclude the activity. Again, it may depend on engagement-to-engagement, but we usually say that our mission has been completed once we have compromised a Domain Admin account or have similar access to the target infrastructure.
Some Common Red Team Exercises:
Usually, red teamers use various tools and techniques to exploit a weakness/vulnerability in a physical infrastructure network. They will use all sorts of techniques from phishing to card cloning and social engineering to fetch any information wherever possible.
Because their main aim is to compromise the whole environment, they will not hesitate to utilize any technique, per rules of engagement. Following are some of the red team exercises that can be done in a corporate environment:
Penetration Testing:
It is an assessment of the host, network, and applications to assess their security posture. Assessor tries to penetrate deep into the target scope and replicate themselves as a malicious actor and try to abuse the target environment as per the engagement rules and regulations.
Social Engineering:
In this activity, Red teamers try to trick employees of the target environment as they are legal authorities or some authoritative personnel and try to fetch as much information as possible.
Phishing:
In this technique, we send malicious emails and text messages to the employee of the target and lure the employees into giving any information, which can be used in the later phase of our testing.
Sniffing:
It is a technique in which we use various tools like Wireshark, TCPDump, etc., to see if we can get any traffic running over HTTP protocol. As you might have known, HTTP protocol is an insecure protocol, and complete communication can be read by any man-in-the-middle attacker. This can sometimes leak a great deal of information like usernames, passwords, secret tokens, etc.
Card Cloning:
We use this technique to clone the cards of a current employee of the organization and try to deceive the physical access control into accessing the unrestricted areas.
Blue Team:
Blue teamers are the defender of any organization. They are responsible for establishing a defense mechanism for any corporate environment or infrastructure. While the Red team put their effort into breaking the controls and defense mechanism in place for any target organization, blue teams put their efforts into placing necessary and optimized controls to make their organization safe.
Due to the increase in cyber threats, blue teams are necessary need for any organization now. In this era of the modern tech world, online businesses only survive when they assure the security of the data they own. Here blue teamers, a.k.a defenders, play their role to ensure all the necessary controls are in place to make the data safe.
Defenders have many frontiers to cover to protect their castle. In addition, there are various job roles and responsibilities that the blue team covers to ensure an organization’s defense.
How Blue Team works:
Unlike Red Team, which follows a generic methodology to achieve their aim, blue teams do not have any generic methods to guard an organization. However, they have various tasks, which further have well-crafted ways that can be used to achieve particular aims. Blue Team tasks may include but not limited to below:
Risk Assessment
In this exercise, defenders map the completely corporate environments as per some well-known security standards like ISO27001:2013, PCI, NIST, etc., and analyze the gaps in their environment. This assessment includes any risks that can directly or indirectly hamper the business of the organization. First, we do the GAP Analysis against some well know IT Security standards. After identifying the gaps w.r.t to Information Security, we analyze the Risk associated with these gaps, accept some risks that we think are not a priority task, and mitigate others by applying appropriate controls as suggested by the framework. For such risks in which we cannot apply the recommended controls as per the framework. We try to push some compensating controls to minimize the risks.
Incident Response Plan
An Incident Response plan is a set of well-documented steps and procedures that needs to be followed in case of any data breaches or cyber incident. We’ll discuss briefly what these steps are and how we can follow them in case of an unfortunate cyber attack:
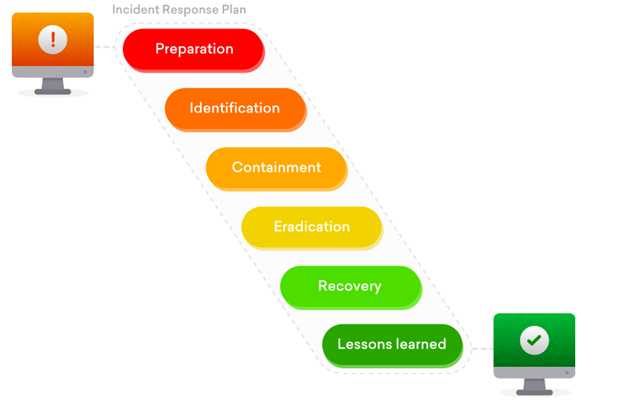
Preparation
In the preparation phase, we have to ensure that our employees know their roles and responsibilities in cyber attacks. We need to make sure that steps are well documented and followed when a cybersecurity incident occurs.
Also, we need to make sure that we do incident response drills annually, if not bi-annually.
Identification
This step is responsible for identifying a security incident. Various questions need to be answered before completing it:
a) What is the timeline of incident?
b) How was it identified?
c) Who identified it?
d) What was the scope of the compromise?
Containment
In this phase, we have established that the security breach has already happened or it is happening. Therefore, our first instinct will be to delete all the malicious activities in such hyper-tensioned scenarios and eliminate the incident.
But this may lead to severe consequences, which may lead to clear out the malicious activity properly. So, rather than this approach, we tend to contain the malware in a restricted environment and analyze its behavior. In this way, we know how the malware is behaving and how it is improvising w.r.t the target environment.
This led to better insights for the blue teamers to analyze what vulnerability was exploited to do this security breach.
Eradication
First, we analyze the malware and get the information we need from this security incident. Next, we move on to clear out our environment from the malware and backdoors this incident might have caused.
Recovery
This is the way toward reestablishing and returning influenced devices into your business climate. During this time, it’s critical to get your frameworks and business activities fully operational again without another break.
Lesson Learned
After the examination, hold a meeting with the Incident Response Team and talk about what you’ve gained from the incident. This is the place where you will dissect and report everything about the incident.
Figure out what functioned admirably in your reaction plan and where there were a few openings. Exercises gained from both false and genuine occasions will help fortify your frameworks against future assaults.
Vulnerability and Patch Management
In this phase, we bi-annually, if not quarterly, assess our assets for potential vulnerabilities that are in our infrastructure. However, as new exploits and vulnerabilities are frequently coming, there is a need to have documented Vulnerability and Patch Management process.
This includes scanning all of the inventories. If the scope is too large, we can do this activity on a sample basis and have a basic idea of the health of our ecosystem.
Once we are done with vulnerability scanning of our inventories, we have to prioritize our efforts in patch management. We can not start patching servers that are not business-critical or not exposed publicly. We have to prioritize our efforts to make sure we address high-priority assets first.
This is an essential task for any organization. It gives a clear picture of our environment in terms of system health.
Conclusion:
In this article, we tried to discuss the day-to-day activities of the Red Team and Blue Team. We also discussed the essential skills required for getting into an entry-level job for each of them. The Red Team aims to compromise the target environment entirely by following a crafted methodology. On the other hand, blue teamers have a lot of work to secure their castle. Blue teamers don’t have a transparent cut methodology which they can follow to defend their asset completely. Still, there are specific exercises they have to do to ensure they secure infrastructure.
In the end, it is good to re-iterate that NO environment is “Hack Proof”. However, we can do our best to minimize the associated risks. Red Team and Blue team are just those tools that can help us improve the security of our enterprise.






 Stateful VS Stateless Firewalls And Why It Matters Which You Choose
Stateful VS Stateless Firewalls And Why It Matters Which You Choose





